Learn about IV management
We already understand that IV stands for intravenous injection, or injection immediately into a vein. We've got a fluid restriction of 3 mL for subcutaneous or intramuscular injections in adults, because exceeding this restriction can cause tissue problems around the injection web page, but because IV injections move directly into the affected person's vein, the handiest problem is the amount of fluid that may be given intravenously is the quantity of fluid that can be consumed by means of someone's body, with out receiving more fluid than the body can soak up or excrete (that may result in such things as coronary heart failure, excessive blood stress, and excess fluid in the lungs). The secure range of each day fluid consumption will range in line with the patient's circumstance, size, and age, as an expansion of scientific situations together with coronary heart failure, kidney failure, for example, diabetes may additionally require patients to limit their daily fluid consumption. The health practitioner need to suggest fluid consumption limits relying at the patient's condition, but for normal wholesome adults, the ordinary variety for total fluid consumption (from intravenous fluids and/or fluids they drink) must be 35-50 ml/kg body weight/day. A 100kg healthful grownup, for example, must devour 3500-5000 ml of fluid an afternoon, or 3.5 to five litres. It is lots of fluid as compared to what we can give with other routes of parenteral administration. The ordinary range for overall fluid consumption (from IV fluids and/or fluids they drink) need to be 35-50 ml/kg frame weight/day. A 100kg wholesome grownup, as an example, should devour 3500-5000 ml of fluid an afternoon, or 3.5 to five litres. It is quite a few fluid as compared to what we are able to supply with different routes of parenteral administration. The normal variety for total fluid intake (from IV fluids and/or fluids they drink) should be 35-50 ml/kg body weight/day. A 100kg wholesome grownup, for example, should eat 3500-5000 ml of fluid a day, or three.5 to 5 litres. It truly is a number of fluid in comparison to what we will deliver with different routes of parenteral administration.
Because of this, IV management is used while we want to present a big quantity of fluid, or while we need to dilute the drug in a huge amount of fluid to present it the right electricity or to save you it from inflicting irritation. Similarly, because IV administration normally includes a bigger quantity of fluid, IV-given drugs are usually infused over a longer time period, usually any time between 15 minutes and a few hours. This is markedly one-of-a-kind from subcutaneous or intramuscular injections, as each involve immediately injecting the whole drug dose.
In addition, IV management is quicker than every other technique of management as it goes without delay into the bloodstream and can consequently be used when rapid drug movement is required.
Fundamental IV Settings
Let's have a look at the maximum fundamental possible placing for IV:
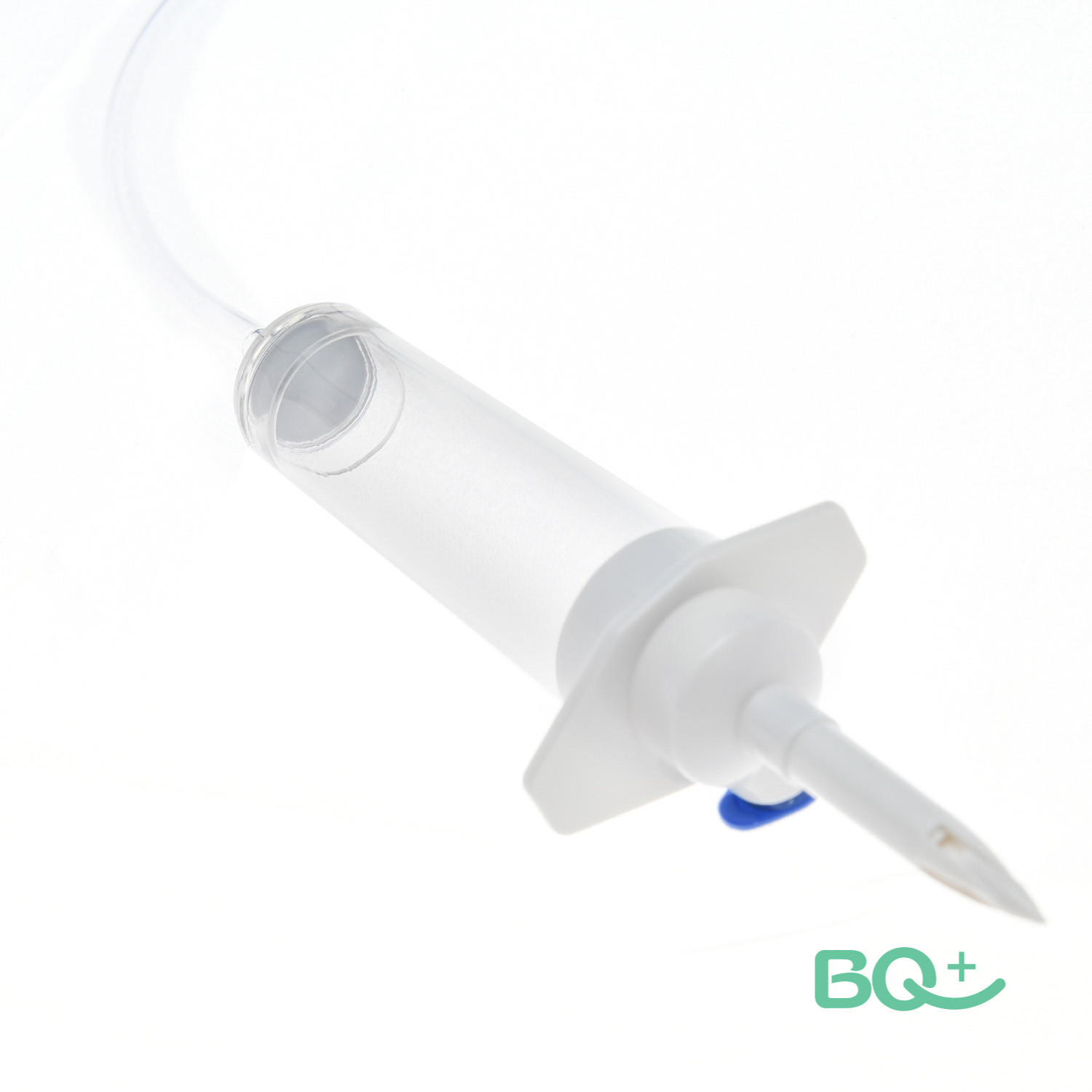
Intravenous injections are most often administered thru pre-mixed fluid luggage. The usual sizes of those bags can variety from 50 ml to 1,000 ml. As proven inside the picture above, the bag is hung from the infusion rod and the infusion line is attached to the lowest of the bag; The IV tube includes several important parts:
The infusion chamber is located directly beneath the IV bag; in this chamber, we will see the liquid dripping from the bag into the IV tube. That is where we measure the rate of the guide IV putting; We checked out the room and counted the drops we saw consistent with minute. As a result, for instance, if we counted 25 drops in 60 seconds, we'd say that IV become infused at 25 drops in keeping with minute or 25 GTT/minute. (In fact, we probable do not remember drops for a whole minute; as an example, we are able to rely the wide variety of drops we see in 15 seconds after which multiply that range by way of 4 to get the variety of drops in a minute.)
The drip should usually be half of full. If the drip chamber is too full, we are able to not be able to see the drops to count them, so we will not be capable of determine the fee of IV infusion. If the drip chamber is not full sufficient, then this can permit air to go into the IV infusion line, because of this air can input the patient's movement, which may be very dangerous and block blood vessels or forestall the coronary heart.
The roller clip is a tool we use to govern the charge of intravenous fluids. If we roll it in a way, it squeezes the IV tube greater tightly, making it narrower and thus allowing the fluid to flow through the tube greater slowly; If we roll it the other manner, it's going to release the squeeze at the IV tube, making the tube less slim and permitting the IV fluid to drift via at a faster charge. So, as an instance, if we found (by way of looking at the injector and counting the drops) that an IV turned into being infused at 50 GTT /min, but it turned into ordered to be infused at 30 GTT /min, we would tighten the roller clamp to sluggish down the drip charge till we could only matter 30 drops in step with minute through the drip chamber.
All curler clamps on a fixed of IV tubes need to be closed before we attach a bag of IV liquid to the top of the tube; This guarantees that no air enters the pipe.
Each intravenous drug is ordered to be infused at a specific fee, and one of the most important tasks of a health facility nurse is to installation the vein so that it is infused at that price, and to alter the vein periodically so that it remains the same whilst the velocity adjustments. At the order rate. The fee at which the IV fluid is injected is called the IV injection rate or go with the flow rate.
The sliding clamp is used when we want to absolutely stop IV drift without adjusting the curler clamp. This is handy if we need to quickly forestall the IV, but we don't want to reset the drift charge by readjusting the roller clamp after beginning the IV again. We do this through last the tube completely as we slide it into the narrowest part of the fixture.
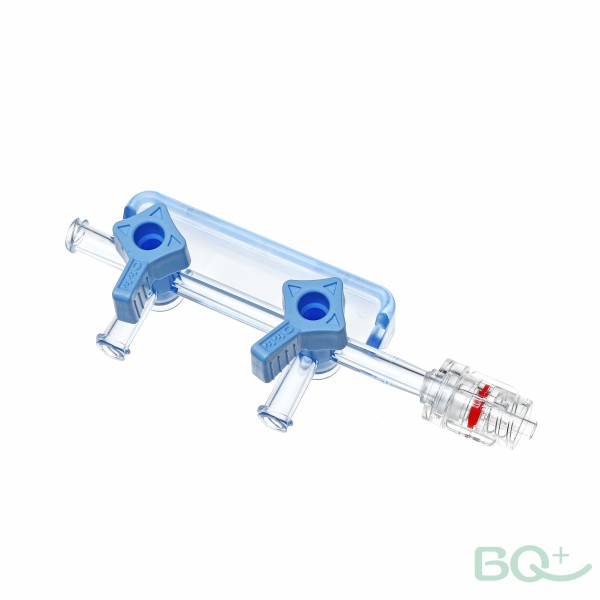
The injection port is a place where medicines or fluids apart from the ones currently within the IV bag may be injected in order that they're infused through the IV tube into the affected person's vein. Within the picture above, we can see two ports: one on the IV bag itself and one underneath the drip chamber. There's usually an injection port close to wherein the needle enters the patient's vein; we will see this under. If we need to mix a drug with the liquid within the IV bag, we use the injection port on the actual IV bag; If we inject the drug into this port after which roll the bag barely to mix the drug into the fluid inside the bag, then the affected person will obtain each the drug and the IV fluids. However, this can only be carried out when blending intravenous fluids and drugs is permitted. If we need to inject the drug immediately or a 2nd IV in order that it does no longer mix with the IV we are already related to, then we will use one of the ports positioned underneath the drip chamber.
How does the peak of the IV bag affect the fee of infusion
Intravenous fluids paintings because gravity pushes fluid down the road into the affected person's veins. The better the bag is hung, the extra the pressure of gravity on the intravenous fluid to drift down the tube; If the IV bag isn't hung high sufficient, the strain due to gravity will not be sufficient to pressure the fluid into the vein. Consequently, all IV baggage should be hung above the affected person's heart to permit sufficient pressure for IV fluid to be injected, and standard technique is to dangle the IV bag as a minimum 3 toes above the person patient's heart to ensure good enough strain. Enough pressure to hold the IV jogging at a consistent rate.
In addition, on account that changing the height of the IV bag alters the gravitational stress on the fluid, a trade in the height of the bag above the affected person's heart will regulate the IV infusion rate. If the IV bag is higher than the affected person's coronary heart, the IV infusion rate will be increased, and if the IV bag is decrease than the patient's coronary heart, the IV infusion charge could be slowed. Because of this option, if the affected person who has been lying down whilst putting the IV then sits up, the IV infusion price could be slowed down because the IV is now closer to the patient's heart. In truth, technically, any small motion or trade in role of the affected person can adjust the speed of IV infusion. Because of this, the IVs are checked regularly to make sure they may be nevertheless being infused at an appropriate rate; commonly as soon as an hour, after any extensive exchange in the patient's function.
Further, nurses ought to be privy to different complications associated with intravenous remedy. Sometimes the needle may additionally detangle from the vein, allowing intravenous fluids to be injected into the encompassing tissue in place of the vein; that is called osmosis. Some fluid may be injected into the tissue instead of the vein, but eventually the IV will stop due to the fact the gravitational stress isn't always enough to triumph over the strain from the surrounding tissue to save you extra fluid from escaping. As soon as the IV penetrates, a brand new IV need to be began at a new location on the patient's frame, and the IV have to be restarted at the proper charge for a given dose. Symptoms of IV infiltration include: pain or discomfort inside the vicinity around the IV needle, swelling in the place, bloodless to the touch,
How is the IV attached to the affected person
A cannula is a hole needle, or greater generally a flexible plastic tube with a needle inserted into a vein; The catheter has been connected to the affected person's arm to prevent the affected person from coming out whilst he actions, and a sterile dressing has been located on the skin puncture in which the cannula is inserted to save you bacterial infection, that is commonly gift on the skin floor, from entering the bloodstream.
There are specific veins that may be used to location cannulas; we will insert the cannula into a peripheral vein, any vein that isn't always inside the trunk, or we will insert the cannula into a bigger, more valuable vein in the chest.
The peripheral line is an intravenous infusion linked to a peripheral vein, that is any vein that is not located in the trunk. These sorts of IVs are commonly inserted into the arm or hand, despite the fact that legs or toes may be used. This is the maximum commonplace type IV.
The peripheral line have to handiest be used for a short period of time, normally 3 days, because if used longer, bacteria commonly gift at the pores and skin can input the blood or tissues surrounding the injection website online and cause infection. Therefore, if a peripheral line is needed for extra than three days, popular technique is to transport the injection web page to a brand new place every three days to prevent contamination. Each the pinnacle and backside images show the perimeter strains.
The primary Line is an intravenous infusion linked to the chest vein. The cannula is commonly inserted via the chest wall or jugular vein, but it is also viable to insert the cannula right into a peripheral vein after which pass the end of the cannula slowly up until it enters the vital vein.
Relevant veins are plenty large than peripheral veins, so when a valuable Line is used and cannulated into the chest or neck, the tube may be wider, so a couple of smaller tubes can be inserted into a bigger tube, so that a couple of intravenous drugs are added immediately and combining isn't allowed. Further, a critical Line enters the veins that convey blood without delay to the heart, so drugs administered this way can be allotted more speedy for the duration of the body. Specially nerve-racking or high concentrations of medication also are more likely to irritate peripheral veins, along with chemotherapy pills and some liquid nutrients, which can be administered centrally while they're too annoying to be administered via peripheral veins.
But, principal Line infusions are also much more likely to motive bleeding and have a much better hazard of contamination due to the fact the contents of the infusions cross directly to the coronary heart, so any bacteria that receives into the infusions fast spreads around the frame; similarly, because the imperative catheter is wider, there may be a higher danger of getting air into the road that might block the vein or prevent the coronary heart, so more air is permitted in (the greater air that gets into the blood, the risk of the vein being blocked or the coronary heart stopping).
Here, we are able to see a photograph of a patient with a principal Line:
Continuous and intermittent intravenous fluids
On occasion intravenous capsules or fluids are given continuously or continuously. However once in a while we may also handiest need to provide sufferers intravenous fluids and/or medication at sure instances; that is called intermittent intravenous fluids. Patients may also acquire non-stop intravenous fluids/medicinal drugs handiest, intermittent intravenous fluids/medicines only, or a aggregate of each.
Patients receiving non-stop IV usually have IV gadgets linked to them, however for patients who need to simplest receive intermittent IV, we can not completely join them to IV gadgets. Instead, what we did changed into insert a cannula into the affected person as shown under so that we ought to connect the IV simplest whilst the patient absolutely acquired the infusion and disconnect it among dosing:
That is an IV tube with an injection port at one give up; This unique injection port is referred to as the infusion port adapter, although it is also normally referred to as a Heplock or saline lock/port due to the fact in an intermittent IV putting, the patient does now not get a consistent go with the flow of fluid via the cannula, so it could come to be blocked with the aid of clotted blood and have to consequently be periodically flushed to cast off it; Heparin (at a awareness of a hundred U/mL) is a drug that prevents blood clotting, and saline or saline are the two fluids used for this rinse, wherein about 1-2 mL of these fluids need to be injected every 6 to eight hours.
Stage II IV or IV knapsack
If the affected person is receiving non-stop intravenous fluids and/or medication and must additionally get hold of a second intermittent infusion, or if the affected person's present day infusion have to be interrupted for a second, greater pressing infusion or infusion, then we are able to want to hook the affected person with a second IV. A secondary IV, additionally called an IV Piggyback, or IVPB, is a 2nd IV drug or liquid that hangs next to the first drug or liquid and is connected to the primary set of IV tubes thru an injection port below the principle IV drip chamber (if we pass the injection port in the primary IV bag, The contents of the primary and secondary infusions can be mixed and infused at the same time, which isn't always what we need).
Minor IVs are commonly used for capsules and commonly comprise smaller volumes than important IVs; Secondary IV bags are usually 50-250 ml, whilst the maximum generally used number one IV baggage are 500 or 1000 ml. In fashionable, secondary I.V. Is an intermittent drug, and we want to interrupt a single I.V. Or non-stop infusion, after which we need to resume the infusion with a unmarried I.V. After the secondary I.V. Is complete. Because we need the secondary vein to be fed first, we should droop the secondary vein above the number one vein. To try this, we attach the extender to the pinnacle of the principle IV bag to lower it in order that the top of the principle IV bag is decrease than the bottom of the auxiliary IV bag (see photo under).
Intravenous push or push
Now and again we might need to offer it by means of IV, perhaps because it's large than 3 mL, or because it's higher absorbed, but we do not offer a massive sufficient extent or a robust sufficient awareness, and we want to provide it long term; We can also most effective want to inject the drug as soon as right away, just as we might with an IM or subQ injection. In this case, we will sincerely inject the drug right into a port on an IV line; A single dose administered by way of placing a syringe into one of the injection ports is referred to as an IV push or BOLus.
We will supply an IV push to a patient who's already in a continuous IV putting, or we can inject an IV push immediately into Heplock that is already set up for intermittent IV management.
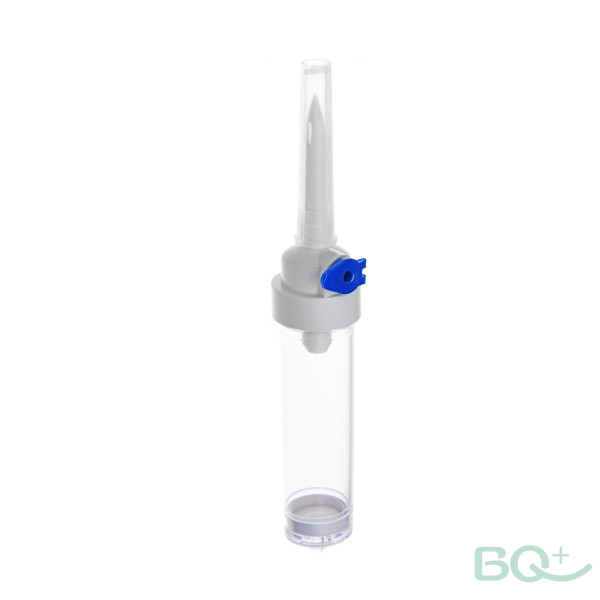
The BQ Medical Drip chamber allows gas to rise from the liquid and estimates the rate of liquid management.Intravenous therapy.
Please click this picture for more information about the Non-vented plastic Spike.↑↑
Please Click this picture for more information about the needle free valve. ↑↑
Please click this picture for more information about the HPM Series.↑↑